This page contains the logos of the partners of the consortium, a brief description of participating organisations and their role in the project. By clicking on the partners’ logo you see their presentation and by clicking on the logo next to the presentation you are redirected to the partner’s site.
BLEMAB Consortium takes advantage of a robust and well-balanced competency integration. It is composed of six partners and two linked parts form four EU country, each contributing specialized expertise at the scientific, technological and technical level, including three institutes for applied R&D (CSM, AMMR, KTH), one national research center (INFN) linked with two universities (UNINA and UNIFI), one university (UNIPD) and one steelmaker (ABG).
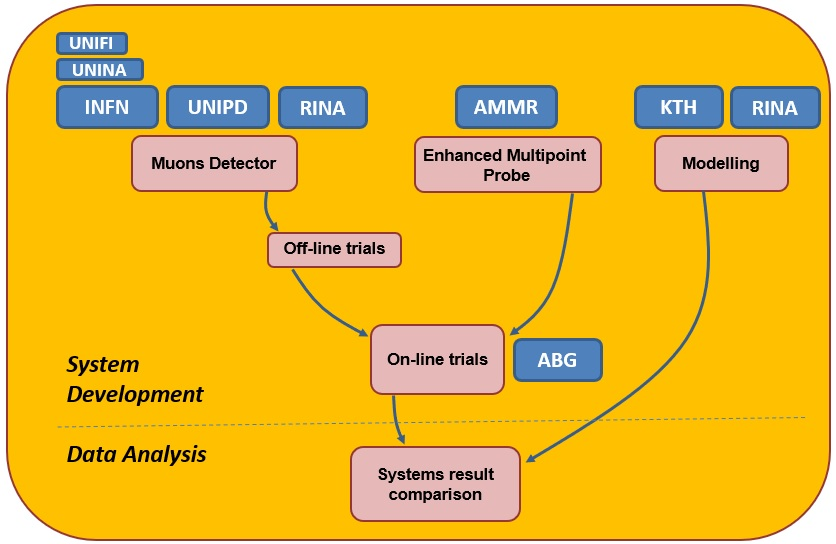
Partners activity interactions:

RINA Consulting – Centro Sviluppo Materiali SpA (CSM): RINA Consulting – Centro Sviluppo Materiali SpA (CSM) is a fully private innovation centre with extensive experiences for the development and application of innovative processes and materials. Today CSM is part of RINA Group that is a global provider of classification, certification, testing, inspection and training services to assist clients in a wide range of business sectors as Marine, Energy, Transport & Infrastructures, Business Assurance, Environment and Innovation. CSM is a leading centre for applied research founded in 1963 by Italy’s major steel industry. Its research activities are mainly related to the modelling and design of materials and products, development of innovative pilot plants and, reduction of environmental impact. With a staff of about 300 researchers, CSM is a private enterprise that ranks amongst Europe’s top Materials Research Centres. The industrial sectors of main interest to the Company are: Energy and environment, Iron and steel, Oil and gas, Aerospace and defence, Mechanics and transport. In particular CSM will be mainly involved in the project with the department of automation and measurements systems (application of visual inspection) with the support of process and modelling departments according to the envisaged industrial applications. In Italy, CSM is active member of national associations and umbrella organizations (Confindustria, AIRI, APRE), and works with the main Italian research bodies (ENEA, CNR, CIRA) and academic world. CSM is high-level participant also in the European Technological Platforms like ESTEP (steel) and EuMat (advanced materials) and also co-founder of RIES (Research Initiative European Steel) for the coordination among the main iron and steel research centers in Europe. The traditional presence of CSM as the Italian reference pole in European research (RFCS and Framework Programmes) results in hundreds of international collaboration agreements and contracts. Currently CSM has more than 80 Grant Agreements active with the European Commission. https://www.rina.org/en/

Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN): INFN, is an italian public-law body founded in 1951. The Institute promotes, coordinates and carries out scientific research in the field of nuclear physics, elementary particles and basic interactions, as well as technological research and development required for activities in above the fields. INFN carries out its activity through 19 units located in the Italian Universities and 4 National Laboratories. The detection of elementary particles has been always one of the major skills of INFN which, in the framework of many international collaborations has realized complex detection systems including mechanics, electronics, data acquisition and data analysis. R&D expertise: The technology proposed for this project hinges on the experience gained by INFN during the design and construction of a large number of wide area muon detectors and associated electronics recently deployed at CERN within the CMS experiment at LHC accelerator. Of interest for the present proposal is also the specific experience of INFN in the field of application of muon-tomography and construction of dedicated detectors as demonstrated in a previous RFCS projects and other projects. https://home.infn.it/it/

Linked part of INFN: University of Firenze (UNIFI) The University of Florence is an important and influential centre for research and higher training in Italy, with 1,800 lecturers and internal research staff, 1,600 technical and administrative staff, and over 1,600 research assistants and doctoral students. It is one of the largest and most productive public research systems in Italy that has assumed the development of internationalization as one of its strategic priorities. Researchers at the University of Florence participate intensively in research programmes of national and international relevance and operate within 24 different departments, having at their disposal approximately 40 research structures comprising inter-departmental and inter-university centres as well as specialized research, knowledge transfer and advanced training centres. The BLEMAB detector will be assembled at the INFN and at the Department of Physics and Astronomy, where also all the relevant component characterization will be performed using the resources and the infrastructure of the Department and of the associated INFN section to which Dr. Lorenzo Bonechi and the members of the team are associated. In the past fifteen years physicists from the INFN together with the Department colleagues after collaborating on various balloon experiments (WIZARD collaboration) have been the main driving force behind the PAMELA experiment which first detected an anomaly in the positron spectra in cosmic rays and in the LHCf experiment at LHC whose forward neutral cross-section measurements are being currently used by theoreticians providing atmospheric interaction models for cosmic ray showers. Moreover, they are currently collaborating on the CALET mission through a research grant awarded by the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The Department itself is situated in new buildings (finished in 2001-2) which host the group’s research laboratories. The group can count on more than five laboratories for a total surface of more than 200 m2 in which the various tasks necessary for the realization of this complex proposal can be performed. Also available to the group is a Class 5000 Clean Room (180 m2) with a high accuracy measuring machine for mechanical prototyping and advanced wire-bonding and technical support for electronics and detector components assembly. This facility was extensively used for years by members of our team both for the LHCf experiment which was assembled in Florence and for the CMS assembly of ten of the sixteen Inner Tracker Cylinders. https://www.unifi.it/

Linked part of INFN: University of Napoli (UNINA) The University of Naples Federico II was established in 1224 through an Imperial Charter of Frederick II Hohenstaufen, King of Sicily and Holy Roman Emperor. It was the first publicly funded university in Europe. Nowadays the university offers courses in essentially all academic disciplines, leading to one hundred fifty-five graduate level degrees. Research facilities provide support to all these courses. Students are given the opportunity to pursue intellectual development as well as the acquisition of professional skills. Current student enrolment nears 86,000 and the academic personnel, at this time, is 2532. The university is made up of three Schools – the Polytechnical and Basic Sciences School, the School of Medicine and the School of Human and Social Sciences – and 26 Departments which operate as semi-independent bodies for the teaching and research management being anyway part of a School. http://www.fisica.unina.it/

University of Padova (UNIPD) The University will take part to the project through the Department of Industrial Engineering, where competences in materials engineering, metallurgy and process modelling via software code , necessary to the aims of the project are available . Mission of the Industrial Engineering Department is the development and technology transfer in the field of Industrial Engineering (Aerospace, Chemical and Materials, Energy and Mechanical). An interdisciplinary approach and constant co-operation with leading foreign Universities and Research Centers grant high international standards in its activities. The department has about 150 faculty persons, including professors, researchers and technical staff and about 100 PhD and post doc positions, with 15 different labs. DII is also involved in about 20 EU research projects and has an annual budget of more than 1 million euros for private/public companies research projects. Key project person will be Irene Calliari (Associate Professor of Metallurgy ) whose research activity is mainly addressed to microstructural characterization of metals, steel physical metallurgy, heat treatment and advanced technique for steel and iron processing investigation with more than 100 published papers. A cooperation with INFN during the RFCS past projects on Muons Tomography (Mu-Steel and Mu-Blast), aimed at exploring the application of the muon scattering tomography to map the distribution of the different components in the burden in the inner zone of the stack in a BF has been established. The role of DII was in developing a software code simulating the passage of muons through a BF model, in adapting the existing muon tomography image reconstruction code to analyze a BF and in giving a metallurgical interpretation of the obtained data. https://www.unipd.it/

Arcelor Mittal Bremen GmbH (ABG): As one of the largest employers in the region, ArcelorMittal Bremen GmbH has state-of-the-art facilities at its disposal that can produce more than 3.6 million tons of crude steel per year. The company is a modern integrated metallurgical plant from pig iron production to sheet metal processing. This enables ABG to guarantee optimum production processes for the automotive and construction industries, packaging market, mechanical engineering. The most important customers include Europe’s leading automobile manufacturers. ABG is located directly on the lower reaches of the Weser on an approx. seven square kilometer site in the north of Bremen. Steel has been produced here since 1957. ArcelorMittal Bremen belongs to the world’s largest steel group ArcelorMittal, whose headquarters are located in Luxembourg. AM Bremen pioneered the long-term use of muon measurements at a blast furnace. These are in operation since 2013. https://bremen.arcelormittal.com/

Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Stockholm is the largest and oldest technical university in Sweden. No less than one-third of Sweden’s technical research and engineering education capacity at university level is provided by KTH. Education and research spans from natural sciences to all branches of engineering and includes Architecture, Industrial Management and Urban Planning. There are a total of 13,400 first and second level students and almost 1,900 doctoral students. KTH has 4,900 employees. The research work of the Materials Science and Engineering Process Unit at KTH is mostly directed towards fundamental research relevant to metallurgical and materials processes, where the unit is known for their realistic phenomena models based on mechanism study from both industrial trials and laboratory experiments. While modelling is a very important tool, the unit is also specialised in conducting experimental laboratory and industrial studies at high temperatures. The unit has extensive experience of running joint projects with partners in industry and research institutes. The unit is currently involved in several RFCS projects as a partner and as a coordinator. Several projects were the unit was involved are completed (e.g. STIMPROVE, BATHFOAM, STEELCLEANCONTROL, ILORA, LADTHERM, BOFDEPHOS, DYNSTIR). The expertise of combining modelling and applied industrial research will ensure the integration of the information obtained by muon absorption and multipoint probe into a standard blast furnace model in order to analyse in particular the burden density distribution, the melting zone and the cohesive zone of the blast furnace. https://www.kth.se/en

ArcelorMittal Maizières Research (AMMR): AMMR is the biggest research centre of ArcelorMittal. AMMR formerly known as IRSID was founded in 1958. AMMR performs research in the whole steel production chain: from mining until the final product. Technical assistance to the ArcelorMittal sites worldwide is another major activity of AMMR. One of AMMR’s core experience and skills is the execution of the multipoint vertical probing trials. AMMR possesses all the necessary resources to maintain and enhance the competencies in the analysis of the blast furnace internal state. In particular, AMMR has its own long-established design office which can engineer the solutions of diverse complexity. The experienced staff performs several multipoint vertical probing trials at different blast furnaces every year. The AMMR researchers have extensive experience in deep analysis of the multipoint vertical probing results and interpretation of the blast furnace operation.